This is the Archived Desktop Edition.
This is the Archived Desktop Edition.
You should be transferred to the Newest Edition for Desktop and Mobile within 2 seconds.
Lesson 2: Temperature
Exercises: Lesson 2
EXERCISES: LESSON 2
INSTRUCTIONS. The following exercises are to be answered by marking the lettered response that best answers the question, or best completes the incomplete statement, or by writing the answer in the space provided. After you have completed all the exercises, turn to "Solutions to Exercises" at the end of the lesson and check your answers.
1. What are two general reasons for taking a patient's temperature?
_________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
2. A person's temperature is considered to be within the "normal" temperature
range if his body temperature is between ________ ºF and ________ ºF.
3. The average body temperature (measured orally) is ___________.
4. The part of the brain that controls the body's heat regulating mechanisms is
called the _____________________.
5. Which type of thermometer will measure a patient's temperature faster?
a. Electric thermometer.
b. Glass thermometer.
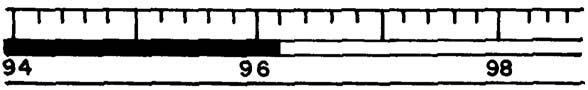
6. What is the temperature reading of the Fahrenheit thermometer shown below?
_________________
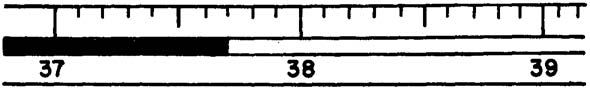
7. What is the temperature reading of the Celsius thermometer shown below?
_________________
8. A glass thermometer is "shaken down" using quick motion of the:
a. Fingertips.
b. Wrist.
c. Forearm.
d. Elbow.
e. Whole arm.
9. Shake down a glass Fahrenheit thermometer until temperature reading is below
_________________ .
10. If you are going to use a model of an electric thermometer that you have not used
before, you should:
a. Guess how it works.
b. Ask the patient if he or she knows how to operate the device.
c. Read the instructions before using the device.
11. List the three areas of the body that are normally used to measure the patient's
body temperature?
a. __________________________________
b. __________________________________
c. __________________________________
12. The bulb of a glass thermometer is long and slender. This thermometer is used to take:
a. Oral temperatures only.
b. Rectal temperatures only.
c. Axillary temperatures only.
d. Rectal and axillary temperatures.
e. Oral and axillary temperatures.
f. Oral, axillary, and rectal temperatures.
13. Oral thermometers are color-coded__________ while rectal thermometers are
color-coded ____________.
14. A rectal temperature reading will be about ____________than an oral
temperature reading for the same patient.
a. 1º F higher.
b. 3 º F higher.
c. 1º F lower.
d. 3º F lower.
15. An axillary temperature reading will be about _________ than an oral temperature
reading for the same patient.
a. 1º F higher.
b. 3º F higher.
c. 1º F lower.
d. 3º F lower.
16. Certain conditions or situations contraindicate taking an oral temperature. Place
an "X" in the blank in front of each condition which indicates that an oral
temperature should not be taken.
a. ____ The patient is 19 years old.
b. ____ The patient is unconscious.
c. ____ The patient can breath through his nose.
d. ____ The patient is mentally confused.
e. ____ The nurse tells you that the patient's temperature is to be taken rectally.
f. ____ The patient finished smoking a cigarette about ten minutes ago.
g. ____ Your orders do not state how the patient's temperature is to be taken.
h. ____ The patient has a cardiac (heart) condition.
17. You have just placed an oral glass thermometer under the patient's tongue and
the patient is securing the thermometer's position with his lips. How long should
you wait before reading the thermometer?
a. At least 30 seconds.
b. At least 1 minute.
c. At least 3 minutes.
d. At least 5 minutes.
e. At least 10 minutes.
f. At least 30 minutes.
18. Place an "X" in the blank in front of each condition which contraindicates taking a
rectal temperature (that is, indicates that a rectal temperature should not be taken).
a. ____ The patient has recently undergone oral surgery.
b. ____ The patient has recently undergone rectal surgery.
c. ____ The patient has hemorrhoids.
d. ____ The patient has just finished drinking a hot cup of coffee.
e. ____ The patient has a cardiac condition.
19. When taking the rectal temperature of an adult, the thermometer should be
inserted to a depth between ______ and ______ inches and held in place for
_______ minutes.
20. When taking the rectal temperature of an infant, the thermometer should be
inserted to a depth of ______ and ______ inches and held in place for ______
minutes.
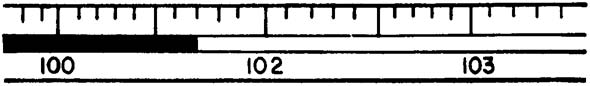
21. Record the rectal temperature shown below in the following blank. ___________
22. Before inserting the probe of the electric thermometer into the patient's rectum,
the probe cover should be:
a. Moistened with sterile water.
b. Lubricated with a jelly or oil.
c. Removed from the probe.
d. Wrapped in sterile gauze.
23. Before inserting the probe of the electric thermometer into the patient's rectum,
you should have the patient:
a. Lie on his side and flex his top knee.
b. Lie on his side and flex his bottom knee.
c. Stand up, then bend as far forward as possible.
d. Lie on his back, bring both knees up to his chest, and wrap both arms around
his legs in order to maintain this position.
24. When taking a patient's axillary temperature, you should leave the thermometer
in place for at least _______ minutes.
25. The thermometers must soak in the disinfecting solution for a minimum of
______ minutes.
Check Your Answers on Next Page