Special Surgical Procedures II
LESSON 1: Eye, Ear, Nose, and Throat (EENT) Surgery
Section I: EYE SURGERY
1-15
1-15. PROCEDURES IN THE TREATMENT OF CATARACT
a. General. Cataract is a clouding or an opacity of the crystalline lens, its capsule, or of both. A cataract may result from local or systemic disease, from eye injury, or the cataract may be congenital. Cataracts seen in the elderly are referred to as primary or senile cataracts. Medical treatment of cataracts is not available. Only surgical removal of the lens is of any significant assistance and this is indicated when the patient's vision is sufficiently depressed.
b. Operative Procedures.
(1) Discussion, or needling of lens. The capsule is incised and the lens substance is broken up. The aqueous humor exerts a solvent action on the exposed lens tissue, thus a clear opening for the passage of light is obtained. The principal use for needling is in cases of cataract due to trauma and in cataract surgery performed on children.
(2) Iridectomy. A sector of the iris is removed as a preliminary step in extraction of the cataract (lens extraction).
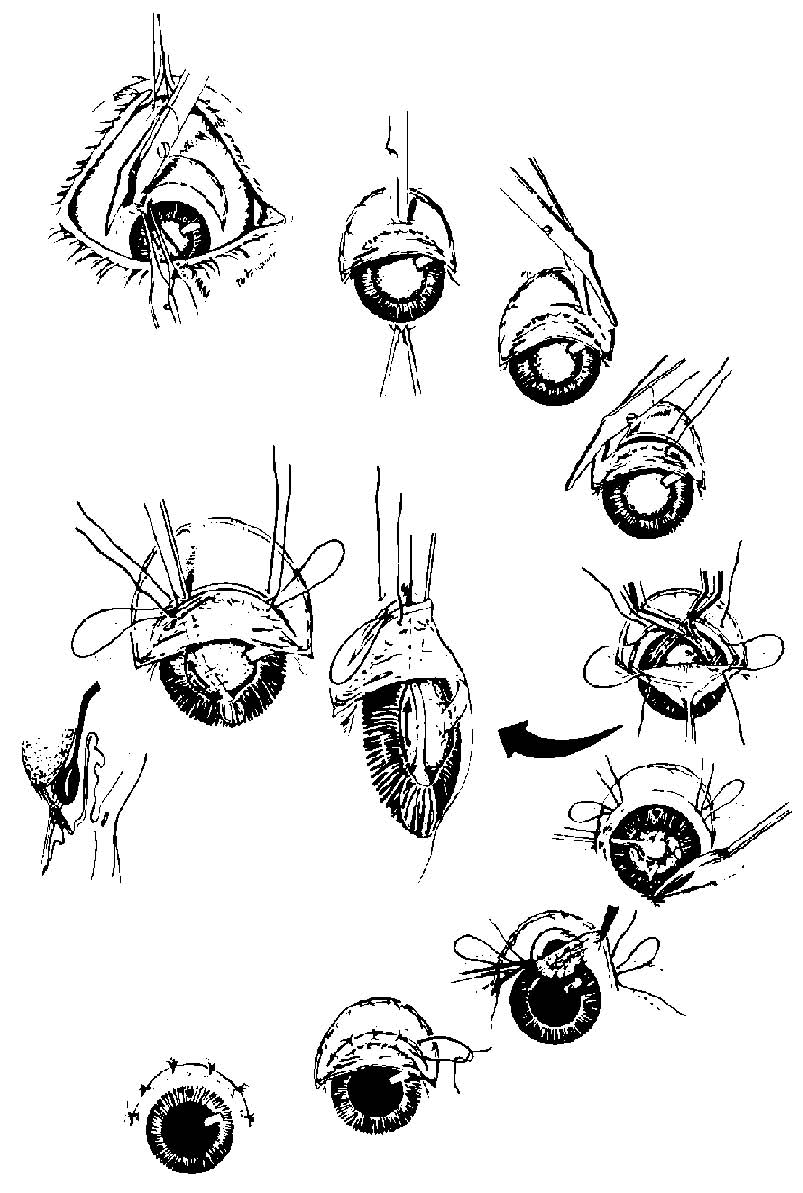
(3) Lens extraction, intracapsular. The entire lens within the capsule is removed intact through a corneoscleral incision (see figure 1-4).
Figure 1-4. Intracapsular lens extraction.
(4) Lens extraction, extracapsular. The anterior capsule is cut, and the lens substance is delivered through the opening in the capsule. The posterior lens capsule is left in place. Therefore, in extracapsular cataract extraction, the major portion of the lens is removed but some remnants of the lens tissue remain.
c. Precautions After Surgery. After surgery, the patient is usually kept at bed rest for a short period, then gradually allowed to ambulate, depending on postoperative conditions. All patients are generally cautioned not to stoop over, lift heavy objects, or strain themselves physically. This warning is maintained during the time when the wound is healing.