1-54
1-54. RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
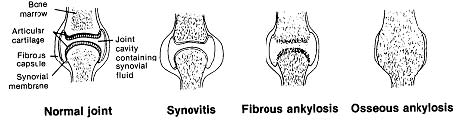
a. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, progressive disease that affects the cartilage surface of the joints and other collagen tissues throughout the body. It is characterized by recurrent inflammation of the lining of joints (synovitis). This leads to formation of a tissue that adheres to the opposite joint surface, inhibiting motion (fibrous ankylosis). The restricting band of tissue becomes calcified, causing destruction of the joint (osseous ankylosis). See figure 1-21.
Figure 1-21. Pathological changes in rheumatoid arthritis.
b. Signs and symptoms of early stage rheumatoid arthritis are:
(1) Paresthesia (burning, prickling sensation).
(2) Anorexia.
(3) Night sweats.
(4) Generalized weakness.
(5) Warm, swollen, and painful joints.
(6) Mild to moderate pain.
c. Signs and symptoms of late stage rheumatoid arthritis are:
(1) Joint stiffness, especially in the morning.
(2) Muscular atrophy around the affected joint, leading to deformity.
(3) Chronic pain.
(4) Multiple organ involvement (pericarditis, osteoporosis, anemia, subcutaneous nodules, vasculitis, neuropathy, fibrotic lung disease).
d. Buffered or enteric coated aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are given to decrease the inflammation that is causing the pain and destruction of the joint. If conservative treatment fails, adrenocortico-steroid drugs are given. Treatment will not reverse the structural damage incurred.
e. Nursing care implications include administering anti-inflammatory drugs as prescribed, providing hot or cold applications as ordered, assisting the patient with exercises, properly positioning the patient with pillows or sandbags to prevent and correct contracture deformities, and educating the patient regarding the disease.