This is the Archived Desktop Edition.
This is the Archived Desktop Edition.
You should be transferred to the Newest Edition for Desktop and Mobile within 2 seconds.
Basic Patient Care Procedures
2-2
2-2. BODY POSTURE AND BODY MECHANICS
Through the knowledge of the correct application of their own muscles, medical nursing personnel can instruct patients on how to use theirs. The combination of good posture and body mechanics benefits both medical personnel and the patients.
a. Posture. Posture is body alignment. It refers to the relative positions of the body when lying down, standing, sitting, or any other activity. Posture determines the stress and the strain on muscles and the distribution of weight. It affects the pressure on many of the organs of the body. Posture also affects such important functions of the body as circulation, respiration, and digestion as well as actions of the joints. To attain good posture, which requires the least strain to maintain, the following respective positions should be practiced.
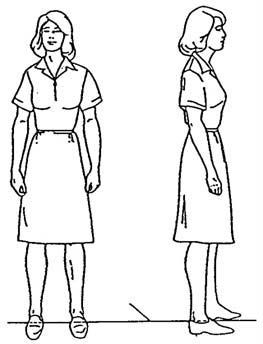
(1) In a standing position, the back should be straight; feet firmly on the ground, about 4 to 6 inches apart to give an adequate base of support, with the toes pointing straight ahead or slightly toed out; head and rib cage held high; chin, abdomen, and buttocks pulled in; and knees slightly bent (figure 2-1).
(2) In a sitting position, the back should be straight, with the weight resting equally on the buttocks and under surface of the thigh, but not on the base of the spine (figure 2-2).
Figure 2-1. Standing position. Figure 2-2. Sitting position.
b. Body Mechanics. Body mechanics is the coordinated use of the body parts to produce motion and to maintain balance. The use of good body mechanics promotes the efficient use of muscles and conserves energy. The following principles apply to any moving or lifting activity:
(1) Face the direction of movement.
(2) Use large muscle groups of the legs, arms, and shoulders to lessen the strain on the back and abdominal muscles.
(3) Bring the object to be lifted or carried as close to the body as possible before lifting. (This keeps both centers of gravity close together.)
(4) Bend the knees and keep the back straight when leaning over at work level.
(5) Kneel on one knee, or squat, and keep the back straight when working at the floor level.
(6) Push, pull, slide, or roll a heavy object on a surface to avoid unnecessary lifting.
(7) Obtain help before attempting to move an obviously unmanageable weight.
(8) Work in unison with an assistant. Give instructions and agree on the signal to start the activity.