Treating Chemical and Biological Agent Casualties
Lesson 1: Chemical Agents and Protection From Chemical Agents
1-13
1-13. DETECTION EQUIPMENT
Soldiers on the battlefield need to detect chemical agents. They may use detector papers to detect and identify liquid chemical agents. At squad, crew, or section level, the M256-series chemical agent detector kit has the ability to detect and identify field concentrations of nerve, blister, and blood agent vapors.
a. Chemical Agent Detector Paper. Two types of chemical agent detector paper are issued to soldiers. ABC- M8 VGH chemical agent detector paper, called M8, which detects and identifies liquid agents, and the M9 chemical agent detector paper that detects the presence of chemical agents. The M9 DOES NOT identify chemical agents.
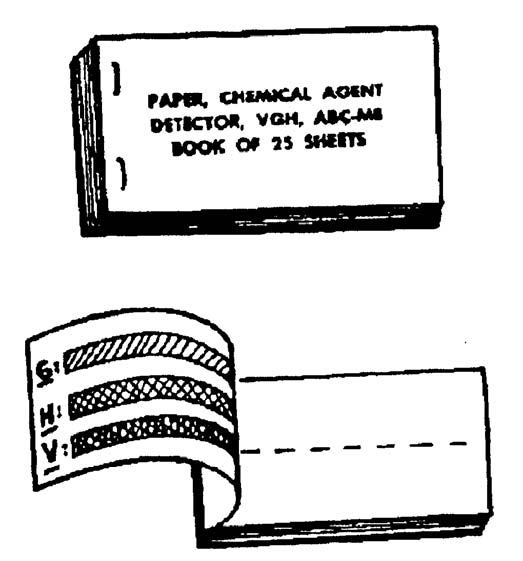
(1) The M8 chemical detector paper (figure 1-7) comes in booklets of 25 sheets. It will detect and identify liquid V- or G- type nerve agents or H- type blister agents. These sheets are impregnated with chemical compounds that turn dark green, yellow, or red when they come in contact with a liquid chemical agent. Your booklet has a color chart that will help you determine which chemical agent has been contacted.
Figure 1-7. ABC-M8 chemical agent detector paper.
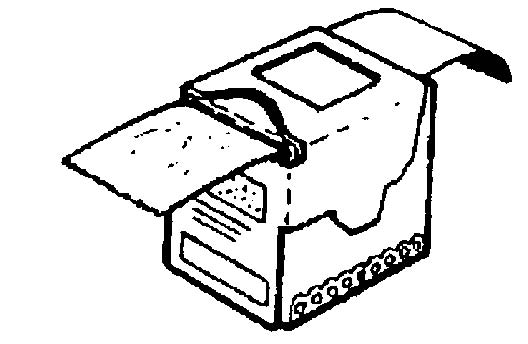
(2) M9 chemical detector paper (figure 1-8) is used to detect the presence of liquid chemical agents. It does not detect chemical agent vapor. When the paper turns red or reddish color, it indicates the presence of a nerve agent (G and V) or a blister agent (H and L). M9 paper should be read only with a source of white light.
Figure 1-8. M9 chemical agent detector paper.
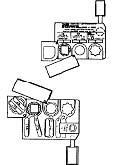
b. M256-Series Chemical Agent Detector Kit. The M256-series chemical agent detector kit (figure 1-9) is issued to squads, crews, or sections. The kit provides the squad level ability to detect and identify field concentrations of nerve, blister, or blood agent vapors. The kit can differentiate between classes of agents which helps unit leaders determine when unmasking may be safe after a chemical attack. The M256 consists of 12 individually packed samplers/detectors, a set of instruction cards, and a packet of ABC-M8 VGH chemical detector paper.
Figure 1-9. M256-series chemical agent detector kit.