Principles of Epidemiology and Microbiology
Lesson 3: Practical Application of Microbiology
Section III: Packing Microbiological Specimens for Shipment
3-7
3-7. IMPORTATION AND INTERSTATE SHIPMENT OF HUMAN PATHOGENS AND RELATED MATERIALS
It is frequently necessary to ship specimens to reference laboratories for analysis or confirmation. Acceptable shipping containers and procedures for packing specimens are described below:
a. Noninfectious Specimen.
(1) Enclose the specimen in a sterile glass container and cap. A screw-capped test tube or jar is satisfactory.
(2) Place the glass container in standard double shipping containers.
(3) Pad the spaces between the containers to guard against breakage.
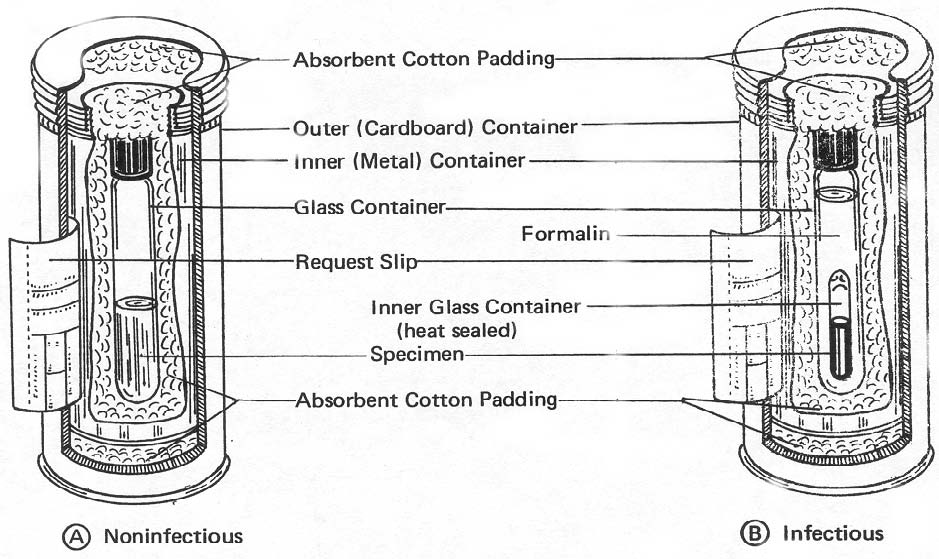
(4) The properly packed container of noninfectious material will have the following layers, from specimen outward: specimen, glass, padding, metal, padding, and heavy cardboard (figure 3-5(A) ).
Figure 3-5. Microbiological specimens picked for shipment.
b. Infectious Specimen.
(1) Enclose the specimen in a sterile, stout glass tube, and seal the ends of the tube by fusion of the glass.
(2) Place the glass tube containing the specimen in a stout glass container that can be sealed by an insulated screw cap, rubber stopper, or by fusion of the glass.
(3) Add formalin to the outer container so that the inner glass container is surrounded by formalin; then seal the glass container with wax. This procedure provides for disinfectionís if the inner container should break.
(4) Pack this double glass container in standard double shipping containers.
(5) Pad the spaces between the containers to guard against breakage.
(6) The properly packed container of infectious material will have the following layers, from specimen outward: specimen, glass, formalin, glass, padding, metal, padding, and heavy cardboard (figure 3-5 (B) ).
c. Additional Requirements.
(1) The importation or subsequent receipt of etiologic agents and vectors of human disease is subject to the Public Health Service Foreign Quarantine Regulations (42 CFR, Section 71.156).
Permits authorizing the importation or receipt of regulated materials and specifying conditions under which the agent or vector is shipped, handled, and used are issued by the Centers for Disease Control.
(2) The interstate shipment of indigenous etiologic agents, diagnostic specimens, and biological products is subject to applicable packaging, labeling, and shipping requirements of the Interstate Shipment of Etiologic Agents (42 CFR Part 72). Packaging and labeling requirements for interstate shipment of etiologic agents are summarized and illustrated in figure 3-5.
(3) Additional information on the importation and interstate shipment of etiologic agents of human disease and other related materials that may be obtained by writing to:
Centers for Disease Control
Attention: Office of Biosafety
1600 Clifton Road, N.E.
Atlanta, Georgia 30333
Telephone: (404) 329-3883
FTS: 236-3883