Principles of Epidemiology and Microbiology
Lesson 2: Public Health Microbiology
Section I: Introduction
2-3
2-3. TYPES OF CELL REPRODUCTION
a. General. Growth and reproduction are accomplished by means of cell division. One of the characteristics of cells is their ability to reproduce their own kind of division. This does not mean, of course, that the cells of a mouse will divide and produce another mouse. It does mean, however, that tissue cells in a certain part of a young mouse will divide to form additional cells of the same type, thereby producing growth in the organ made up of that particular tissue. In the case of microscopic, unicellular organisms, cell division produces a new organism.
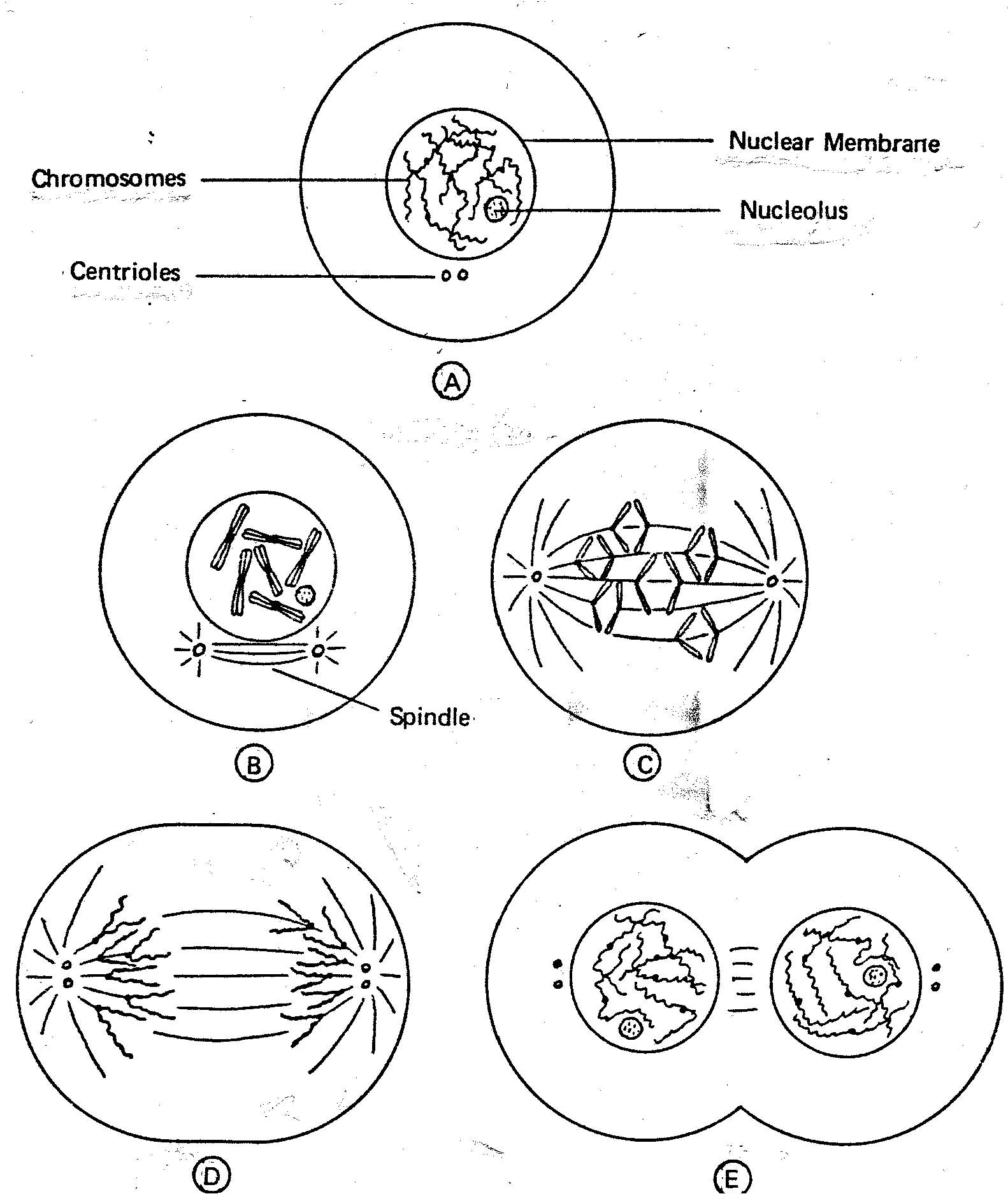
b. Mitosis. Mitosis is a complicated form of cell division found primarily in the higher forms of life, but which may occur in some of the lower forms, such as certain protozoa. In mitosis (figure 2-3), the chromatin becomes organized into pairs of chromosomes and the centrioles (comprising the centrosome) begin to move toward opposite poles, forming a spindle. The nuclear membrane and nucleolus break down, the centrioles reach opposite poles, and the pairs of chromosomes separate, moving along the spindle toward the poles. After reaching the poles, the chromosomes consolidate each centriole forms a new centriole, two new nucleoli, and nuclear membranes are formed. When cell division is complete, each new cell is ready to undergo the same process.
Figure 2-3. Types of cell reproduction-mitosis.
c. Meiosis. Meiosis is similar to mitosis, but the chromosome pairs do not separate as in figure 2-3. Instead, half of the chromosomes go to each centriole, resulting in two new cells having half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This type of cell division is found only in the sexual cells of the higher forms of life. The cells formed by meiosis are known as gametes. When two gametes of opposite sexes of the same species combine, they form a zygote, which contains the same number of chromosomes as each parent cell and half of the hereditary characteristics of each.
d. Amitosis. Amitosis is a simple type of cell division in which the nucleus undergoes cleavage, followed by that of the cytoplasm, without the formation of a spindle and the alignment and polarization of chromosomes (figure 2-4). Each cell receives a copy of the parent chromosomes. Amitosis is rare in the higher forms of life, but it may occur in the lower forms.
Figure 2-4. Types of cell reproduction-binary fission.
e. Binary Fission (Transverse Fission). Binary fission is the simplest form of cell division and that most frequently seen in the study of microbiology. Binary fission normally occurs when a cell reaches an optimum size and environmental conditions are favorable. The center of the cell constricts, a new cell membrane (or cell wall) forms between the two portions of the cell, and cleavage occurs, forming two new cells. A copy of the chromosome is produced so that each new cell has the same genetic information. Figure 2-4 is a graphical representation of binary fission.